Identity Based Profile¶
On the evan.network a profile is simply a Data Contract. The data can initially only be edited by the owner of the profile but when permissions are granted other members can also edit the data.
An identity based profile is also a data contract but the owner of the data contract is another contract which we shall call the identity contract. The previous implementations were all account based profiles on the evan.network but now all new users will be using identity based profiles.
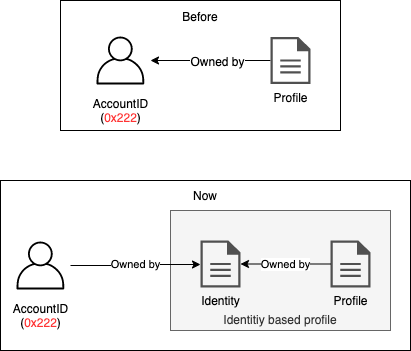
identity based profile
When an account requests for an identity based profile, several steps occur:
- a new identity smart contract (VerificationHolder) is generated
- a new profile smart contract (Data Contract) is generated
- identity contract becomes owner of profile contract and is mapped in a registry (V00_UserRegistry) as such
- requesting account becomes the owner of this identity
When using identities we will come across three important terminologies. activeIdentity and underlyingAccount and activeAccount. A single user can have multiple identities and the identity being used is known as the activeIdentity. The account which is used to execute the transaction for the identity is known as the underlyingAccount. Finally the label activeAccount is a bit older and had been used before transactions were done through identities. It was a mixture of activeIdentity (as it was the acting instance) and underlyingAccount (as it was the account paying for transactions). The usage of activeAccount is by now deprecated in favor of the more specific terms activeIdentity and underlyingAccount.
Furthermore these identities can be converted into DIDs using the DID module and they can issue and be issued verifiable credentials using the VC module.
Configuring to use identity based profile¶
Identity based profiles are the entities which act on behalf of an account. All transactions are done via the the underlying account for the identity however the transaction objects are prepared using the identity. Configuring a runtime to use identity based profile is similar to the process of creating a runtime which uses account based profile as discussed in (getting started)[/getting-started.html#create-a-new-profile-on-evan-network-via-api]
// require blockchain-core dependencies
const Web3 = require('web3');
// require blockchain-core
const { Ipfs, createDefaultRuntime } = require('@evan.network/api-blockchain-core');
const runtimeConfig = {
// account map to blockchain accounts with their private key
accountMap: {
'ACCOUNTID':
'PRIVATE KEY',
},
// key configuration for private data handling
keyConfig: {
'ACCOUNTID': 'PASSWORD',
},
// use identity flag for using identity based profiles
useIdentity: true,
// ipfs configuration for evan.network storage
ipfs: {host: 'ipfs.test.evan.network', port: '443', protocol: 'https'},
// web3 provider config (currently evan.network testcore)
web3Provider: 'wss://testcore.evan.network/ws',
};
async function init() {
// initialize dependencies
const provider = new Web3.providers.WebsocketProvider(
runtimeConfig.web3Provider,
{ clientConfig: { keepalive: true, keepaliveInterval: 5000 } });
const web3 = new Web3(provider, null, { transactionConfirmationBlocks: 1 });
const dfs = new Ipfs({ dfsConfig: runtimeConfig.ipfs });
// create runtime
const runtime = await createDefaultRuntime(web3, dfs, { accountMap: runtimeConfig.accountMap, keyConfig: runtimeConfig.keyConfig, useIdentity: runtimeConfig.useIdentity });
console.dir(runtime);
}
init();
Now you can use an a runtime object which uses an identity as an execution point to interact with the evan.network blockchain. Remember to use runtime.activeIdentity when you want to specify who is doing an an action when using the API.
getRuntimeForIdentity¶
getRuntimeForIdentity(existingRuntime, identity)
Creates a runtime for a specific identity, based on another runtime. The context of this runtime needs a profile with the corresponding encryptionKeys saved using setIdentityAccess or the correct set encryptionKey within the runtime.keyConfig.
Parameters¶
existingRuntime-Runtime: existing runtime instanceidentity-string: identity address
Returns¶
Promise returns Runtime: runtime instance for identity
Example¶
await getRuntimeForIdentity(runtime, identities[1]);